Year 2013 has been an eventful year in the healthcare industry. HHS (Health and human services) issued set of modifications to the HIPAA privacy and security rules assuring enhanced protection for patients’ protected health information. Quick adoption of EHRs (electronic health records) in the wake of the HITECH Act and the phenomenal growth in remote monitoring capabilities—specifically mhealth, made the news. Serious talks were delivered on the importance of liquid data within healthcare organizations accelerating their journey to an effective and efficient personalized care. And we also heard about Google Glass being the potentially transformative new gadget that could revolutionize healthcare soon.
The healthcare IT landscape is evolving and the market is on an upswing for sure. To keep pace with the rising tide, it may be worthwhile to have a quick look at some of the healthcare IT trends predicted by the experts and industry analysts for the year 2014.
1- Mobile healthcare- The Rising Star
Mobile healthcare also termed as m-Health by many, is rapidly gaining interest amongst the consumers and the developer fraternity. The m-Health market, consisting of medical devices like cardiac monitors, diabetes management devices, Wearable fitness tracking devices and healthcare applications is estimated to be valued at $6.6 billion in 2013 and is expected to reach $20.7 billion by 2018 at a healthy CAGR of 25.5%, according to research report.
With growing number of healthcare apps in app stores and increased awareness of the benefits of preventive and wellness oriented programs, m-Health has the potential to transform the healthcare industry.
ISV’s in the healthcare domain may find better acceptance rates for integrated m-Health applications, which can seamlessly interact with other devices, apps and are able to share data to provide comprehensive healthcare.
2- BYOD- Clinical Staff Embracing Tablets & Smartphones in their Workflow
Healthcare industry has been no different than any other in the mixed interest shown towards Bring Your Own Device (BYOD). The administrators are skeptical of it citing security concerns, whereas doctors and nurses have been championing towards the cause due to increased flexibility and mobility provided in their workflow with usage of tablets and smartphones.
Benefits of BYOD in healthcare include but not limited to better access to patient information resulting in enhanced medical care to improved communication and cost savings.
Healthcare organizations considering the growing wave of mobile users will need to outline a good BYOD policy which also caters to and are in compliance with HIPAA and HITECH requirements.
3- Data Security – Privacy and Integrity of Data to be a Prime Concern
Healthcare industry deals with extremely sensitive data and with the recent changes to HIPPA under the HITECH act has made data security a top concern/priority for Healthcare CIO’s. Security administrators will need to work harder to strike a balance between adequately protecting the confidentiality and integrity of patient information and at the same time ensure ready access to the data to authorized personnel.
4- Interoperable IT environment – Healthcare Information Exchange Standards to get a push
Healthcare information exchange (HIE) is the capability to mobilize healthcare information electronically among incongruent healthcare information systems within a region, community or hospital system, while upholding the meaning of information being exchanged.
The healthcare industry is striving towards developing an environment of interoperability amongst healthcare information systems, where the healthcare data can move freely, be accessed and analyzed by various systems in secured way to provide timely and efficient patient centered care, irrespective of vendor producing the electronic health record (EHR) data.
To achieve this, the industry is pushing for standardization in recording of patient data and for IT solutions to have interoperable frameworks to facilitate secured retrieval and access of data.
5- Big data Solutions – Adoptions to increase
With the advent of digitized patient data in form of EHR’s and host of data collected from wearable medical devices, healthcare industry can definitely benefit from Big Data technology.

We have recently highlighted how Big data analytics can help in healthcare industry. The decision making in healthcare can be improved substantially by using Big Data Technologies. Using Hadoop eco system, health care providers can now process massive data sets to see the evidences and arrive at correct decision faster than before.
Leading research firm Gartner states that Healthcare industry is second in terms of investments planned during the next two years (2014-15) for Big Data.
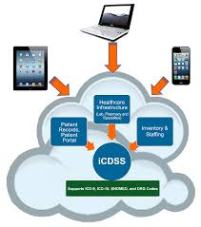
6- Clinical Decision Support Systems- Increase in Implementations
A clinical decision support system (CDSS) is a knowledge based application which analyzes data to help healthcare providers make better decisions. It is an adaptation of the decision support system (DSS) commonly used to support business management.
As stated in the above trend, patient data in digitized form is now available and hence constitutes as the essential data supply for these decision support systems. Also the Centre for Medicare and Medicaid services (CMS) in its meaningful use stage 3 wants hospitals to increase use of CDSS.
The demand to utilize these data mass to help healthcare personnel arrive at better decisions is growing.
7- Healthcare Data in Cloud- Migration to Increase
Organizations across the healthcare industry are looking towards Cloud computing offers in this turbulent transition phase towards IT. Cloud offers flexible storage facilities for ever-increasing clinical data and solves the challenge involving access and sharing of this data across various systems and geographies without significant costs and infrastructure investment.
Research firm IDC states that the cloud presents strong opportunities for healthcare providers to create efficiencies, flexibility, and agility while increasing service levels for applications.
We could surely see healthcare institutions migrate more and more data into the cloud in a bid to comply with regulatory requirements and also to drive down their operational costs and improve healthcare delivery.
The above mentioned trends depict a very exciting transformational direction for healthcare industry. It will be interesting to see how Big Data transforms the healthcare industry with its key insights and actionable information and how m-Health improves patient well being.
References:
http://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/2593815
http://www.healthit.gov/providers-professionals/how-attain-meaningful-use
http://www.emrapproved.com/what-is-emr.php
http://searchhealthit.techtarget.com/definition/clinical-decision-support-system-CDSS